Hungary education system

1. Key features of the Education System
Governance, supervision, maintenance and establishment
Central educational governance or supervision basically are under the auspices of two ministries, namely the Ministry of Interior (public education) and the Ministry of Culture and Innovation (higher education, vocational education and training). The Ministry of Technology and Industry is responsible for adult education. Vertical governance is divided between the central (national), territorial, and to some extent, institutional levels in VET and public education.
The maintenance of kindergartens is a municipal task.
In 2013, the maintenance of municipal schools was taken over by a central state institution maintenance center. The Government has established a national body, the Klebelsberg Center, to coordinate the maintenance of public education institutions. This Center brings together the School District Centers.
A VET institution operating as part of a VET Center is an organizational unit of the VET Center with legal personality. In case of a public VET institution, governing powers are exercised by a designated member of the Government on behalf of the State. Non-state VET institutions are maintained by the Founder themselves or the managing competences are exercised on behalf of the founder, by another person appointed by the Founder.
In case of a higher education institution, the person exercising the founding rights performs the tasks related to the maintenance of the higher education institution.
Public/general education institutions can be established and maintained by
- the state
- minority self-governments
- churches as legal persons
- religious associations or
- a natural person or an organization.
VET institutions can be established individually or jointly by
- the state
- minority self-governments
- churches as legal persons or religious associations
- business organizations
- foundations
- associations
Higher education institution can be founded independently or together with another entity, by
- the Hungarian state
- minority self-governments
- churches as legal persons
- business organizations with seat in Hungary
- foundations, trust foundations, public foundations, religious associations registered in Hungary.
Organisation, structure, assessment and evaluation
Education and training can take place in general (kindergarten and school) education, vocational education and training, higher education and adult education.
General education institutions, basically, are kindergartens (óvoda), basic schools (általános iskola), upper secondary grammar schools (gimnázium), upper secondary vocational grammar schools (szakgimnázium), vocational special schools (szakiskola) and skills development (special) schools (készségfejlesztő iskola).
VET institutions can be technicums (technikum) and vocational schools (szakképző iskola).
A higher education institution can be a university or a college.
A legal person, any entity – having legal capacity according to personal law -, a sole proprietor or a natural person engaged in economic activities may operate as an adult education provider, in addition to public entities (VET institutions) providing adult education.
In accordance with the Public Education Act, all students are assessed annually regarding their reading, math, and science skills in grades 6, 8, and 10.
Since 2015, an annual language assessment has also been conducted in English and German as the first foreign language in grades 6 and 8.
Every year, the Educational Authority organizes a (targeted) language assessment for students of bilingual schools in grades 6 and 8.
Pupils in full-time school education annually take part in physical condition and fitness tests from the 5th grade onwards.
Every public education institution, their principals and teachers are regularly evaluated. A central body, the Educational Authority, is responsible for this evaluation.
A central administration body responsible for VET carries out the external evaluation of the QA system of VET institutions.
The Hungarian (Higher Education) Accreditation Committee is an independent national expert body established for the external evaluation of the operation of the internal QA system of the higher education institution.
In case of adult education providers, the central state administration body for adult education has control powers.
Early school leaving
The proportion of early leavers from education and training (refers to a person aged 18 to 24 who has completed at most lower secondary education and has not been involved in further education or training in the last four weeks) was 12% in Hungary in 2021. The European Union’s goal is to reduce the value below 9% by 2030.
Teaching Profession
The qualification required of teachers in kindergartens and in the first four grades of basic schools (ISCED 0 and 1) is a BA in kindergarten education and a BA in primary education. The requirement for teachers teaching at lower secondary level is either a bachelor’s degree or a master’s degree, but recent teacher (teaching in secondary education) graduates of the new teacher education system can only obtain a master’s degree in teaching. Teachers teaching at upper secondary level are required to hold a master degree diploma.
VET is performed by the so called “oktatók” (educators) in VET institution. Teachers of general subjects shall hold
- a university degree or, with the exception of basic school teachers, a master’s degree, in technicums.
- at least a college-level specialist teacher qualification -corresponding to the taught subject- in vocational schools (szakképző iskola).
As a general rule, VET teachers shall hold
- a master’s degree in VET teaching or any higher education degree with a sector specific qualification -in technicums.
- a sector specific higher education qualification or any higher education degree with a sector specific qualification -in vocational schools (szakképző iskola).
Instructors of practical skills are required to have at least a Matura certificate and a sector specific qualification.
The teaching positions that can be established in a higher education institution are an assistant lecturer, an assistant professor, a college or university associate professor, a college or university professor and a master lecturer. The requirement for an employment in an adjunct position is to obtain a doctoral degree. The requirement for an employment in a college or university professor position is that the Prime Minister appoint the candidate as a college professor and the President of the Republic of Hungary appoint the candidate as a university professor.
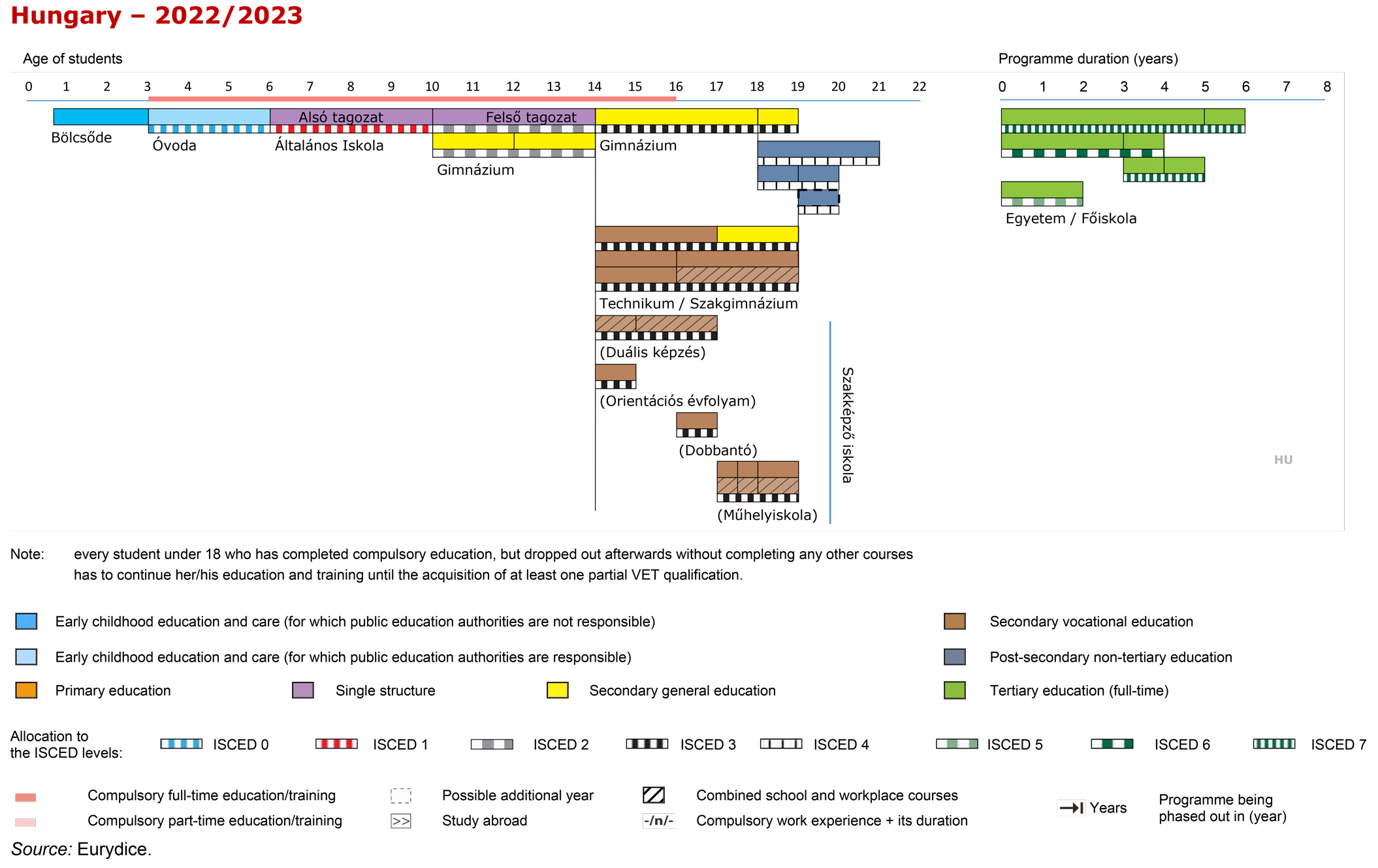
2. Levels of the Education System
Participation in education and training is compulsory between the ages of 3 and 16 (the academic year in which the student completes it). However, the completion of an ISCED level 3 school program in a reasonable time, the acquisition of the first two professions, including the related preparatory years and participation in a school workshop programme, is free (for a maximum of three years in the case of the second profession). The state also provides the first vocational qualification related to vocational training free of charge until the first qualification exam.
The duration of the programmes:
- ISCED 0: 3 years
- ISCED 1: 4 years
- ISCED 2: 4 years
- ISCED 3: 2-5 years
The first institution that the child may attend is the crèche (bőlcsöde), whose provision is integrated in the basic child welfare care system (not public education) and undertakes the day care, the professional specialist care and the education of children aged between 20 weeks and 3 years.
The kindergarten provides institutional education for children aged 3-6 years. Kindergarten education is compulsory from the age of three.
Compulsory school education starts at the age of six, provided that they have reached the necessary level of development -required to start their school education. Compulsory schooling lasts until the end of the school year in which the student completes the age of 16.
Basic education in Hungary is mostly provided in 8-year basic schools (single structure) and provides a foundation of general education for the 6–14-year-olds. After that, students can continue their mainstream studies in an upper secondary institution (ISCED 3): in an upper secondary grammar school, an upper secondary vocational grammar school, a technicum and a vocational school.
The upper secondary grammar school (gimnázium) provides general education, mostly for 4-years (but there are also 6- and 8- grade/year high schools) and prepares for matura/upper secondary school leaving examination. This examination is also an admission test to higher education institutions.
Upper secondary vocational grammar schools (szakgimnázium) are educational institutions providing five year long programmes specialized in arts, pedagogy or general knowledge, in these schools general education and vocational education and training are provided in four grades/years, and only vocational education and training in the fifth year.
Technicums (technikum)
- provide general education, preparing student both for the matura examination and the vocational examination, and enables students to continue their studies in a higher education institution or to start working.
- or provide exclusively vocational education and training for student holding a matura certificate.
The number of grades to fulfil studies is included in the Register of Vocational Occupations.
Technicum may organize two year general education programme to help students obtain the matura certificate.
Vocational schools (szakképző iskolák)
- provide general education and vocational education and training required for the acquisition of a given profession, or
- prepares students for the VET exam only
The number of grades to fulfil studies is included in the Register of Vocational Occupations.
The institutional system of higher education consists of public and non-public universities and colleges, which offer bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral courses, as well as higher education vocational training courses. In the split training system, the 6-8 semester bachelor’s degree training programme cycle is followed by the 2-4 semester master’s degree training cycle. The first cycle provides degrees (baccalaureate, bachelor of science, bachelor of profession, bachelor of arts) and professional qualification. A master’s degree (magister, master of science, master of profession, master of arts) and professional qualification can be obtained in the master’s programme. The training is undivided (10-12 semesters) in some study fields, so e.g. in the medical, legal, or teaching profession sectors.
Planned and recently introduced reforms and policy measures are set out in the Ongoing Reforms and Policy Developments chapter.
3. Structure of the National Education System
4. Common European Reference Tools Provided by the Eurydice Network
- National Student Fee and Support Systems
- Organisation of the Academic Year in Higher Education
- Organisation of School Time in Europe (Primary and general secondary education)
- Recommended Annual Instruction Time in Full-Time Compulsory Education in Europe (Presented by grades/stages for full time compulsory education as well as by subject and country.)
- Teachers and School Heads Salaries and Allowances in Europe (Salaries and allowances of teachers and school heads at pre-primary, primary, lower secondary and upper secondary education levels.)
Source: https://eurydice.eacea.ec.europa.eu/national-education-systems/hungary/overview
Follow us on social media: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube.